Divisions on curbing plastic waste persist as UN treaty talks begin

At COP29, Kenya, France and Barbados floated setting up a series of global levies on certain sectors that could help ramp up the amount of money that could be made available to developing countries seeking support to aid their clean energy transition.
As delegates from 175 countries gathered in Busan, South Korea on Monday for the fifth round of talks to secure an international treaty to curb plastic pollution, lingering divisions cast doubts on whether a final agreement is in sight.
South Korea is hosting the fifth and ostensibly final UN Intergovernmental Negotiating Committee (INC-5) meeting this week after the previous round of talks in Ottawa in April ended without a path forward on capping plastic production.
More To Read
- We tested if a specialised magnetic powder could remove microplastics from drinking water: The answer is yes
- How Nigeria’s plastic waste could enrich the fashion industry
- Wajir rallies to end plastic pollution with bold eight-day clean-up campaign
- NEMA launches crackdown on factories producing plastic bags
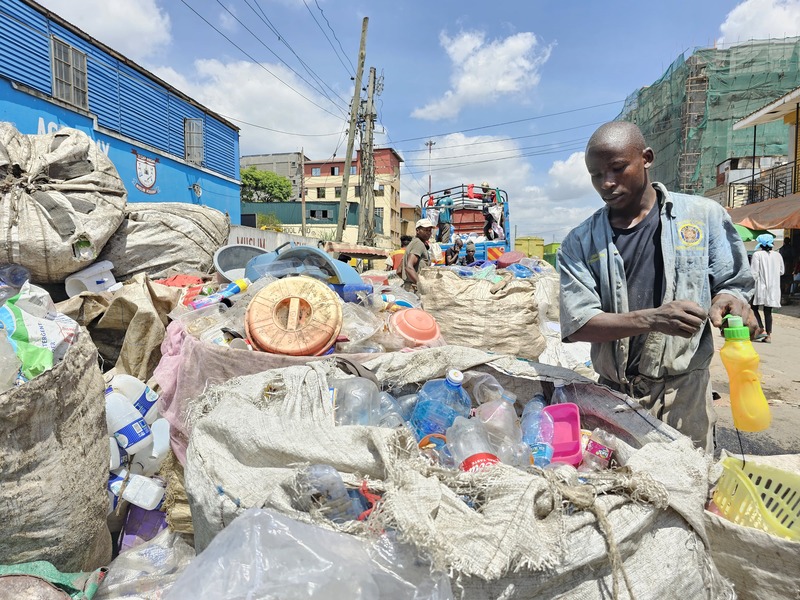
- Unseen and unprotected: The hidden workforce battling Kenya’s waste crisis
- The recycling dilemma: Most plastic still ends up as waste
Instead, the meeting issued a direction for technical groups to focus on chemicals of concern and other measures after petrochemical-producing countries such as Saudi Arabia and China strongly opposed efforts to target plastic production.
The United States raised eyebrows in August when it said it would back plastic production caps in the treaty, putting it in alignment with the EU, Kenya, Peru and other countries in the High Ambition Coalition.
The election of Donald Trump as president, however, has raised questions about that position, as during his first presidency he shunned multilateral agreements and any commitments to slow or stop U.S. oil and petrochemical production.
The U.S. delegation did not answer questions on whether it would reverse its new position to support plastic production caps. But a spokesperson for the White House Council on Environmental Quality said it "supports ensuring that the global instrument addresses plastic products, chemicals used in plastic products, and the supply of primary plastic polymers. "
Inger Andersen, executive director of the U.N. Environment Programme, said she was confident the talks will end with an agreement, pointing to the communique from the Group of 20 nations at a summit last week calling for a legally binding treaty by the end of this year.
 Climate activists march on a street to demand stronger global commitments to fight plastic waste at the upcoming fifth session of the Intergovernmental Negotiating Committee (INC-5), in Busan, South Korea, November 23, 2024. (Photo: REUTERS/Minwoo Park)
Climate activists march on a street to demand stronger global commitments to fight plastic waste at the upcoming fifth session of the Intergovernmental Negotiating Committee (INC-5), in Busan, South Korea, November 23, 2024. (Photo: REUTERS/Minwoo Park)
"This is a very powerful message," Andersen told Reuters in Baku, on the sidelines of the UN climate negotiations, before travelling to Busan for the talks. "We know that it is often down to the wire, but if there is a will, I think we will get there."
Health impact
Sivendra Michael, Fiji's climate minister and chief climate and plastics negotiator, said a global plastics treaty is crucial for a Pacific island country like Fiji to protect its fragile ecosystem and public health.
He told Reuters on the sidelines of the 29th UN Climate Change Conference (COP29) this month that despite not producing any plastic, Fiji is bearing the brunt of its downstream pollution.
"Where do these plastics end up? It ends up in our oceans, in our landfills, in our backyards. And the impact of the plastics breaking down into little substances has detrimental effects, not only on the environment, but on us as individuals, on our health," he said, noting studies that showed most of the fish consumed in the country was polluted with microplastics.
While supporting an international treaty, the petrochemical industry has been vocal in urging governments to avoid setting mandatory plastic production caps and focus on solutions to reducing plastic waste, like recycling.
"We would see a treaty successful if it would really put ... emphasis on ending plastic pollution. Nothing else should be the focus," said Martin Jung, president for performance materials at chemical producer BASF.
Previous talks have also discussed searching for forms of funding to help developing countries implement the treaty.
At COP29, France, Kenya and Barbados floated setting up a series of global levies on certain sectors that could help ramp up the amount of money that could be made available to developing countries seeking support to aid their clean energy transition and cope with the increasing severe impacts of climate change.
The proposal included a fee of $60-$70/ton on primary polymer production, which is on average around 5-7% of the polymer price, seen potentially raising an estimated $25-$35 billion per year.
Industry groups have rejected the idea, saying it will raise consumer prices.
Top Stories Today